Introduction to the Mediterranean Diet
In the realm of dietary regimens, the Mediterranean diet stands out as a beacon of health and longevity. This diet, deeply rooted in the culinary traditions of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, has garnered widespread acclaim for its myriad health benefits. Our comprehensive guide delves into the Mediterranean diet’s core principles, backed by scientific evidence, and reveals how it can significantly enhance your overall well-being.
Key Components of the Mediterranean Diet
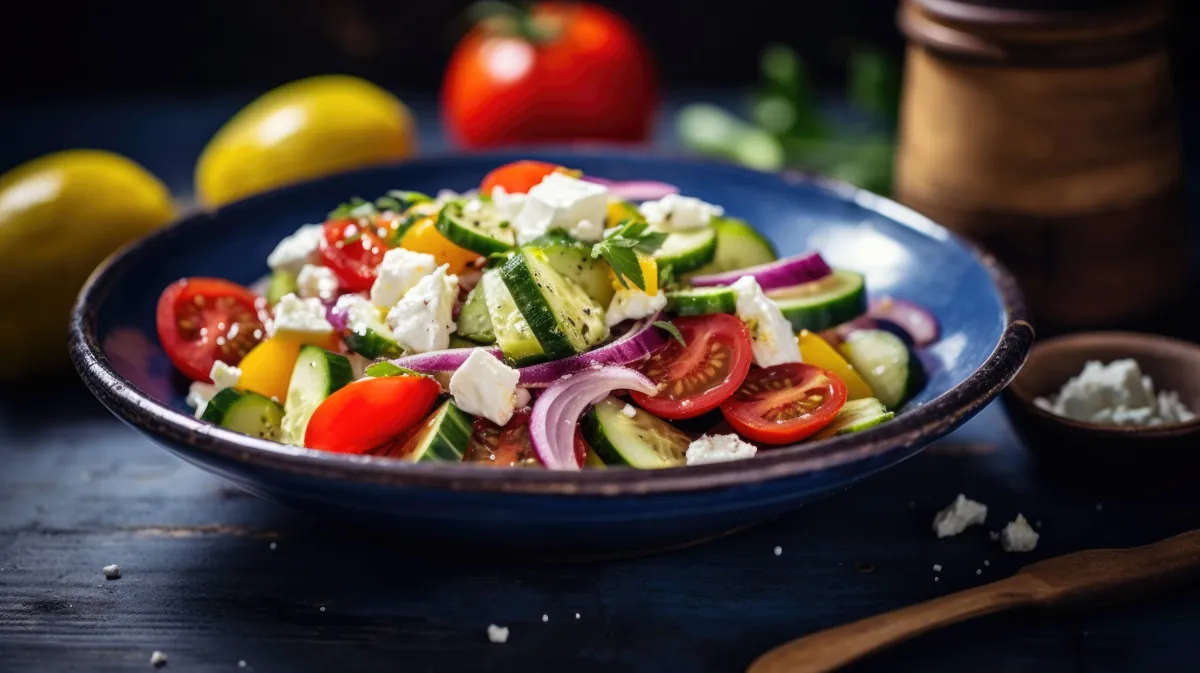
Plant-Based Nutrition
The Mediterranean diet is predominantly plant-based, featuring an abundant intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts. These foods are not only nutrient-rich but also high in dietary fiber, antioxidants, and a plethora of vitamins and minerals essential for optimal health.
Healthy Fats
A hallmark of the Mediterranean diet is its emphasis on healthy fats, particularly those sourced from olive oil, seeds, and nuts. Unlike saturated fats found in red meat and dairy products, these monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats contribute to heart health and help in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels.
Moderate Consumption of Seafood
Seafood, particularly fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, is a vital component of the Mediterranean diet. Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, seafood consumption is linked to reduced risks of heart disease and improved brain health.
Limited Intake of Red Meat
The Mediterranean diet recommends only occasional consumption of red meat. When consumed in moderation, it ensures a balanced intake of proteins without the adverse effects associated with high red meat consumption, such as increased risk of heart disease and certain cancers.
Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet
Cardiovascular Health
Numerous studies have established the Mediterranean diet’s efficacy in reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. It lowers the likelihood of developing conditions like hypertension, high cholesterol, and coronary heart disease, primarily through its emphasis on healthy fats and a plant-based diet.
Diabetes Prevention
The diet’s low reliance on processed sugars and high fiber content plays a crucial role in preventing Type 2 diabetes. Natural sweeteners like honey and the primary use of fruits for sugar significantly reduce the risk of developing this chronic condition.
Gut Health
The Mediterranean diet’s fiber-rich components, such as beans, lentils, and whole grains, foster a healthy gut microbiome. This not only aids in digestion but also plays a critical role in disease prevention and overall health maintenance.
Cancer Risk Reduction
Adherence to the Mediterranean diet has been linked to a lower risk of several types of cancer, including breast, colorectal, and lung cancer. The diet’s rich antioxidant content is a key factor in its cancer-preventive properties.
Cognitive Benefits
Emerging research indicates that the Mediterranean diet may also benefit cognitive health, potentially reducing the risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. The antioxidants present in fruits and vegetables are believed to protect brain cells from damage.
Implementation Strategies
Embracing Whole Foods
Switching to whole, unprocessed foods is a fundamental step in adopting the Mediterranean diet. This involves choosing fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and legumes over processed alternatives.
Incorporating Healthy Fats
Replacing saturated fats with healthier options like olive oil not only enhances the flavor of meals but also contributes to heart health. Including nuts and seeds as snacks or meal components adds both nutritional value and satiety.
Enjoying Seafood Twice a Week
Incorporating seafood into meals at least twice a week can significantly boost omega-3 fatty acid intake, vital for heart and brain health.
Cooking and Seasoning Techniques
The Mediterranean diet encourages cooking methods that preserve the nutritional value of food, such as grilling, baking, and sautéing. Seasoning with herbs and spices instead of salt enhances flavors while reducing sodium intake.
Conclusion: A Lifestyle Choice
Adopting the Mediterranean diet is more than a dietary change; it’s a lifestyle choice that embraces healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, and an overall balance in life. While it may not be a quick-fix solution for weight loss, its benefits for long-term health and well-being are profound and well-documented.
By incorporating the Mediterranean diet into your daily routine, you not only improve your physical health but also embark on a journey towards a more balanced and fulfilling life.